- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- The Accounting Process
The Accounting Process
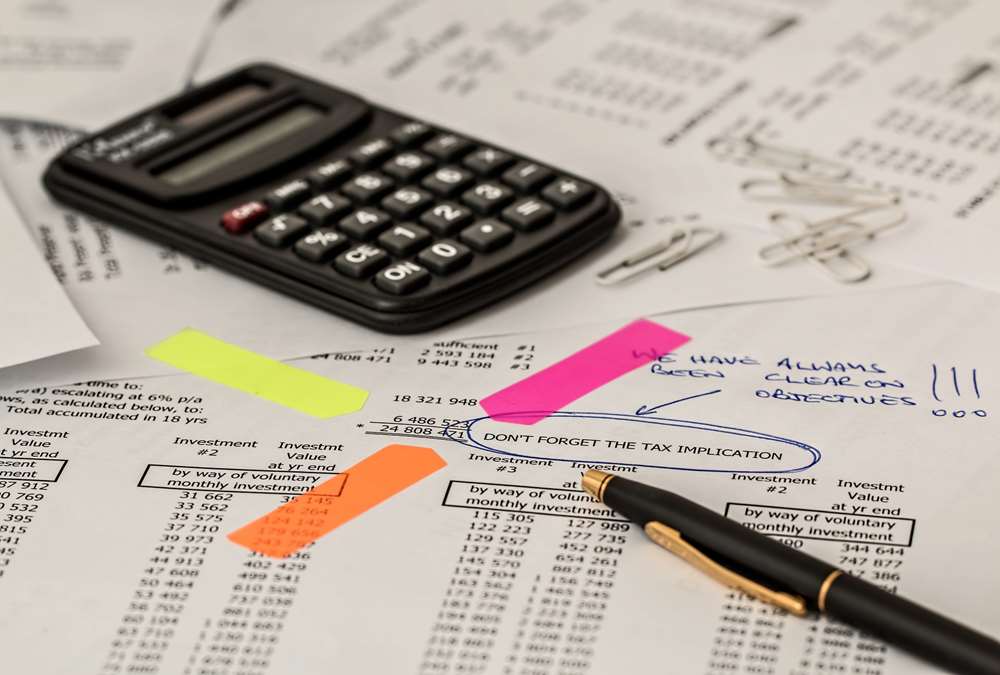
In this article we will focus on and understand the accounting process which enables the accounting system to provide the necessary information to business stakeholders. We will deep dive into each of the steps of accounting and will understand how to identify accounting transactions and the process for recording accounting information and transactions.
In this article, we will focus on and understand the accounting process which enables the accounting system to provide the necessary information to business stakeholders. We will deep dive into each of the steps of accounting and will understand how to identify accounting transactions and the process for recording accounting information and transactions.
Step 1: Identifying Business Stakeholders:
A business stakeholder is a person or entity having an interest in the economic performance of the business. These stakeholders normally include the owners, managers, employees, customers, creditors, and the government.
1. Owners of the Business:
The owners who have invested resources in the business clearly have an interest in how well the business performs. Most owners want to get the most economic value for their investments and they want to maximize the total economic worth of the business. This economic worth includes results of past profits and also reflects prospects for future profits.
2. Managers & the Management:
The managers are the individuals who have been authorized to operate the business on a day to day basis. They are responsible for various functions of the business as per the agreed roles and responsibilities between them and the owners. Managers are primarily evaluated on the economic performance of the business and therefore they also have an interest in maximizing the economic performance of the business.
3. Employees:
The employees provide services to the business in exchange for a paycheck. The employees have an interest in the economic performance of the business because their jobs depend upon it. The better is the economic performance of the business the more security and compensation it offers to the employees.
4. Customers:
The customers usually also have an interest in the continued success of a business. For example, if the company fails on economic performance it may not be able to fulfill its promised obligations making the customers suffer.
5. Creditors:
Like the owners, the creditors invest resources in the business by extending credit, such as a loan or supplying material on credit. They have an interest in how well the business performs because there recovery of credit/investment depends on the capability of the business generating enough cash to pay them back.
6. Governments:
Various governments and statutory bodies have an interest in the economic performance of businesses. Central and State governments collect taxes from businesses within their jurisdictions. Statutory bodies levy various taxes that are based on the economic performance of the business. The better a business does, the more taxes these bodies can collect.
Step 2: Understanding Accounting Needs:
The accounting process starts with the identification of its stakeholders. Discussion in the last paragraph will help you understand who could be a stakeholder for your business and identify the correct stakeholders. The next step in the accounting process is to assess the various information needs of those stakeholders and design the accounting system to meet those needs.
Step 3: Identifying Accounting Transactions:
The next step is to identify the events and activities that have an economic or monetary impact that is to identify accounting transactions. Every economic activity conducted within a business has a direct or indirect effect on the finances of the company. These economic transactions need to be recorded. The accounting process begins with identifying which transactions to record. For economic activity to be considered a transaction, it must be able to be expressed in monetary terms. Also, transactions must be related to the business – stakeholders' or owners' private expenses are never included with business transactions.
Step 4: Recording Transactions:
The next step in the accounting process is to record business activity by entering what accounts a transaction affects and how. Recording transactions includes documenting revenues (by invoices or sales receipts), and entering purchases (in the account payable account) and expenditures (in the check register). This step sometimes also involve high-level accounting tasks, such as recording sales orders, tracking prospective customers, and projecting sales opportunities and cash flow.
To record and classify a transaction to appropriate accounts, a proper understanding of the accounting equation is and accounting standards and practices is a must. Calculating and summarizing transactions in a traditional accounting system is a tedious process and automated accounting frees accountants from these repetitive tasks by calculating and summarizing hundreds or thousands of individual transactions and generating reports to satisfy a variety of stakeholders.
Step 5: Preparing Accounting Reports:
Finally, once the accounting system records the economic data about business activities and events, the next logical step is to prepare the business reports and provide them to the stakeholders according to their informational needs. The double-entry system enables accountants to prepare some standard reports like trial balance, profit, and loss account and balance sheet. Accounting reports are based on generally accepted accounting standards and these reports are powerful tools to help the business owner, accountant, banker, or investor analyze the results of their operations.
Stakeholders use accounting reports as a primary source of information on which they base their decisions. They use other information as well. For example, in deciding whether to extend credit to a company, a banker might use economic forecasts to assess the future demand for the company’s products. The banker might inquire about the ability and reputation of the managers of the business.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles define the accounting procedures, and understanding them is essential to producing accurate and meaningful records. In this article we emphasize on accounting principles and concepts so that the learner can understand the “why” of accounting which will help you gain an understanding of the full significance of accounting.
-
A joint venture (JV) is a business agreement in which the parties agree to develop, for a finite time, a new entity and new assets by contributing equity. They exercise control over the enterprise and consequently share revenues, expenses and assets. A joint venture takes place when two or more parties come together to take on one project.
-
In this article, we will describe how to determine if an account needs adjustment entries due to the application of the matching concept. Learners will get a thorough understanding of the adjustment process and the nature of the adjustment entries. We will discuss the four types of adjustments resulting from unearned revenue, prepaid expenses, accrued expenses, and accrued revenue.
-
Introduction to Organizational Structures
Organizations are systems of some interacting components. Levitt (1965) sets out a basic framework for understanding organizations. This framework emphasizes four major internal components such as: task, people, technology, and structure. The task of the organization is its mission, purpose or goal for existence. The people are the human resources of the organization.
-
In this article, we will explain the general Ledger journal processing flow from entering journals to running the final financial reports. Understand the generic general ledger process flow as it happens in automated ERP systems. The accounting cycle explains the flow of converting raw accounting data to financial information whereas general ledger process flow explains how journals flow in the system.
-
Business Metrics for Management Reporting
Business metric is a quantifiable measure of an organization's behavior, activities, and performance used to access the status of the targeted business process. Traditionally many metrics were finance based, inwardly focusing on the performance of the organization. Businesses can use various metrics available to monitor, evaluate, and improve their performance across any of the focus areas like sales, sourcing, IT or operations.
-
Driving Business Efficiency through Divisions and Departments
In case of a multi-divisional organizational structure, there is one parent company, or head-office. And that parent owns smaller departments, under the same brand name. Dividing the firm, into several self-contained, autonomous units, provides the optimal level of centralization, in a company.
-
The purpose of the general ledger is to sort transaction information into meaningful categories and charts of accounts. The general ledger sorts information from the general journal and converts them into account balances and this process converts data into information, necessary to prepare financial statements. This article explains what a general ledger is and some of its major functionalities.
-
In every journal entry that is recorded, the debits and credits must be equal to ensure that the accounting equation is matched. In this article, we will focus on how to analyze and recorded transactional accounting information by applying the rule of credit and debit. We will also focus on some efficient methods of recording and analyzing transactions.
-
GL - Review & Approve Journals
Review and Approval mechanisms ensure that the accounting transaction is reasonable, necessary, and comply with applicable policies. Understand why we need review and approval processes, what are they, and how they are performed in automated general ledger systems. Learn the benefits of having journal approval mechanisms in place.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved