- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- GL - Accruals and Reversals
GL - Accruals and Reversals
There are two commonly used methods of accounting - Cash Basis and the Accruals Basis. Understand the difference between accruals and reversals. Recap the earlier discussion we had on accruals and reversals and see the comparison between these two different but related accounting concepts. Understand how the action of accruing results in reversals subsequently in the accounting cycle.
What is Accounting Accruals:
There are two commonly used methods of accounting - Cash Basis and the Accruals Basis. In cash basis of accounting, income is recognized in books when it is received in cash, and expenses are offset when they are actually paid.
Contrary to Cash Basis Accounting, in Accrual Basis Accounting, financial items are accounted for when they are earned and deductions are claimed when expenses are incurred, irrespective of the actual cash flow. The Accrual accounting method measures the financial performance of a company by recognizing accounting events regardless of when corresponding cash transactions occur. Accrual follows the matching principle in which the revenues are matched (or offset) to expenses in the accounting period in which the transaction occurs rather than when payment is made (or received).
Accrual Accounting
Accrual accounting is considered to be the standard accounting practice for most companies and is the most widely used accounting method in the automated accounting system. This method provides a more accurate picture of the company's current condition, but as all income and expenses need to be recognized based on their occurrence and matching, it is relatively complex when compared to cash accounting, which recognizes transactions only when there is an exchange of cash. The need for this method arose out of the increasing complexity of business transactions and investor demand for more timely and accurate financial information.
Accrual - Example
To help you understand this concept let’s look at an example. A company has sold merchandise on credit to a customer who is creditworthy and there is the absolute certainty that the payment will be received in the future. The company earns a profit of $500 on the total sales price of $2000. The accounting for this transaction will be different in the two methods. The revenue generated by the sale of the merchandise will only be recognized by the cash method when the money is received by the company which might happen next month or next year. However in the Accrual Method, the revenue will be recognized in the same period, an “Accounts Receivable” will be created to track future credit payments from the customer.
Accrual Concepts
Based on the above discussion now let’s take a look at some accrual/deferral related concepts:
-
Accrued revenue is an asset, such as unpaid proceeds from a delivery of goods or services, when such income is earned and a related revenue item is recognized, while cash is to be received in a later period.
-
Accrued expense, in contrast, is a liability with an uncertain timing or amount, but where the uncertainty is not significant enough to qualify it as a provision.
-
As an accounting practice expense and revenue accruals are reversed in the next accounting period to prevent double-booking of expenses/revenues when they get settled in cash
Concept of Reversals:
At the beginning of each accounting period, there is an accounting practice to use reversing entries to cancel out the adjusting/accrual entries that were made to accrue revenues and expenses at the end of the previous accounting period. The use of Reversing Entries makes it easier to record subsequent transactions by eliminating the possibility of duplication.
-
Reversing entries are made on the first day of an accounting period in order to offset adjusting accrual/provision entries made in the previous accounting period.
-
Reversing entries are used to avoid the double booking of revenues or expenses when the accruals/provisions are settled in cash.
-
A reversing entry is linked to the original adjusting entry and is written by reversing the position of debits with credits and vice versa.
-
The net impact of Original Entry and Reversing Entry on the accounting books is always zero.
-
In Automated Accounting Systems, it is not possible to delete transactions once the posting has been made. In such systems reversals is the recommended way to correct the erroneous entries. An example is that one interface feed has been posted by mistake twice. This has inflated many income expense accounts. A reversing entry with opposite debit and credit amounts to all the impacted accounts will nullify the impact of the mistake.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
When the quantum of business is expected to be moderate and the entrepreneur desires that the risk involved in the operation be shared, he or she may prefer a partnership. A partnership comes into existence when two or more persons agree to share the profits of a business, which they run together.
-
Operational Structures in Business
Large organizations grow through subsidiaries, joint ventures, multiple divisions and departments along with mergers and acquisitions. Leaders of these organizations typically want to analyze the business based on operational structures such as industries, functions, consumers, or product lines.
-
Funds contributed by owners in any business are different from all other types of funds. Equity is the residual value of the business enterprise that belongs to the owners or shareholders. The funds contributed by outsiders other than owners that are payable to them in the future. Liabilities are generally classified as Short Term (Current) and Long Term Liabilities. Current liabilities are debts payable within one year.
-
In every journal entry that is recorded, the debits and credits must be equal to ensure that the accounting equation is matched. In this article, we will focus on how to analyze and recorded transactional accounting information by applying the rule of credit and debit. We will also focus on some efficient methods of recording and analyzing transactions.
-
GL - Different Type of Journals
Two basic types of journals exist: general and special. In this article, the learner will understand the meaning of journalizing and the steps required to create a journal entry. This article will also discuss the types of journals and will help you understand general journals & special journals. In the end, we will explain the impact of automated ERPs on the Journalizing Process.
-
Functional Organizational Structures
A functional organizational structure is a structure that consists of activities such as coordination, supervision and task allocation. The organizational structure determines how the organization performs or operates. The term organizational structure refers to how the people in an organization are grouped and to whom they report.
-
A subsidiary is a company that is completely or partly owned by another corporation that owns more than half of the subsidiary's stock, and which normally acts as a holding corporation which at least partly or wholly controls the activities and policies of the daughter corporation.
-
The sole trader organization (also called proprietorship) is the oldest form of organization and the most common form of organization for small businesses even today. In a proprietorship the enterprise is owned and controlled only by one person. This form is one of the most popular forms because of the advantages it offers. It is the simplest and easiest to form.
-
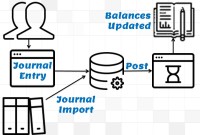
GL - Journal Posting and Balances
In this tutorial, we will explain what we mean by the posting process and what are the major differences between the posting process in the manual accounting system compared to the automated accounting systems and ERPs. This article also explains how posting also happens in subsidiary ledgers and subsequently that information is again posted to the general ledger.
-
The purpose of the general ledger is to sort transaction information into meaningful categories and charts of accounts. The general ledger sorts information from the general journal and converts them into account balances and this process converts data into information, necessary to prepare financial statements. This article explains what a general ledger is and some of its major functionalities.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved