- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Domain Knowledge
- Technology Domain
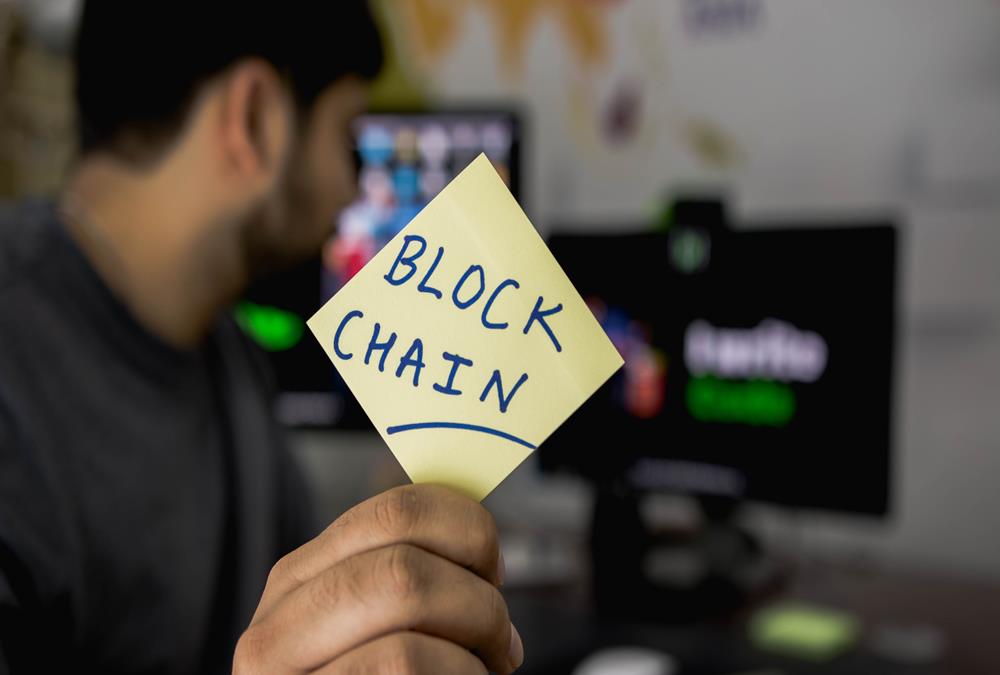
- Block Chain & Distributed Ledgers
Block Chain & Distributed Ledgers
Blockchain is a distributed, decentralized, public ledger. A distributed ledger is merely a type of database spread across multiple sites, regions, or participants. It is a consensus of replicated, shared, and synchronized digital data. Learn more about how the blockchain system is going to change the way you transact business
Introduction
Blockchain leverages Cryptography and hash pointers to create a continuously growing list of records, which are linked to previous blocks, secured using cryptography, contains a hash pointer that establishes links to previous blocks, contain a timestamp and some data.
The use of hash pointers combined with cryptography enables blockchains to become inherently resistant to modification of the data. Sharing blockchain data serves as an open distributed ledger that can record transactions between two parties in a verifiable and permanent way. Any alteration needs a collusion of the network majority.
It’s important to note that for the blockchain to work, the node-to-node network must be motivated and agree to work under ethical standards. Once, and only if, these standards are adhered to, the blockchain could become a powerful tool for improving business, conducting fair trade, democratizing the global economy, and helping support more open and fair societies.
Application of Technology
As Blockchains are secure by design they find a lot of applications for the recording of transactional data, events, medical records, record management activities, and documenting provenance as potential uses. Bitcoin the first digital currency, uses blockchain to maintain its transactions and for solving the double-spending problem without the use of a trusted authority or central server. Blockchain provides transparency, security, and standardization without the use of a central intermediary.
Business Case Example
Venture investment exceeding $1 billion was made in 2015 alone on blockchain technology. The economic and social impact of blockchain’s potential to fundamentally change the way markets and governments work is only now emerging. This revolutionary decentralized blockchain system is going to change one’s life from the way one transacts business or manage assets, to the way one use your machines, vote, rent a car, and even prove the identity. It will have applications in banks and other financial institutions, hospitals, companies, and governments among others.
Financial Services: In traditional financial transactions intermediaries like Banks are often needed to mediate the process and resolve conflicts when a financial transaction takes place between two parties. Blockchain can be used to make the process more transparent, and more effective by introducing products like smart bonds and smart contracts. The former automatically pays bondholders their coupons once certain preprogrammed terms are met. The latter are digital contracts that self-execute and self-maintain, again when terms are met.
Insurance: Claims processing can be a frustrating procedure as insurance processors should validate and approve in midst of fraudulent claims, fragmented data sources, or abandoned policies. The blockchain provides a transparent system by using its encryption properties that allow insurers to capture the ownership of assets to be insured.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Block Chain & Distributed Ledgers
Blockchain is a distributed, decentralized, public ledger. A distributed ledger is merely a type of database spread across multiple sites, regions, or participants. It is a consensus of replicated, shared, and synchronized digital data. Learn more about how the blockchain system is going to change the way you transact business
-
Machine learning (ML) is the process of teaching a computer system on how to make accurate predictions when fed data through the study of computer algorithms that improve automatically through experience. It is a method of data analysis that automates analytical model building
-
An autonomous vehicle (AV), also known as driverless car, robo-car, or robotic car, is a vehicle that is capable of sensing its environment and moving safely with little or no human input. It utilizes a fully automated driving system & how this technology is deployed will change how we get around forever.
-
Internet of Things & Industrial Internet
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) refers to interconnected sensors, instruments, and other devices networked together with computers' industrial applications, including manufacturing and energy management. It brings together brilliant machines, advanced analytics, and people at work.
-
Cloud storage delivers a cost-effective, scalable alternative to storing files on on-premise hard drives or storage networks. Cloud storage is a service that enables saving the data on an offside storage system. Cloud storage is the storage of data online in the cloud
-
Robotic Process Automation is the technology that allows anyone today to create your own software robots to automate any business process. RPA emulate and integrate the actions of a human interacting within digital systems to execute a business process.
-
Robotics is one of the most advanced and emerging technologies that deals with physical robots. Robots are programmable machines that are usually able to carry out a series of functions that can help and assist humans in their day-to-day lives and keep everyone safe.
-
The science of building smart machines capable of performing tasks that makes it possible for machines to learn from experience, adjust to new inputs, and perform human-like tasks. Learn about implications for our future its applications
-
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is a transformative approach to industrial production, by adding layer-upon-layer of material, a computer-controlled process that creates three-dimensional objects shaped into the desired product by parts of it being removed in a variety of ways.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved