- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Domain Knowledge
- General Ledger
General Ledger

General Ledger – Record to Report Process
The ‘Record to Report’ process, also referred to as ‘Account to Report’ or simply as general ledger process, refers to the maintenance of the general ledger right from recording of transactions to preparation of unit trial balances and reporting company’s consolidated financial results.
Bookkeeping is a critical accounting activity that provides the solid financial foundation on which an organization stands. The correctness and integrity of the financial statements that an organization produces largely depend on the correctness and integrity of its bookkeeping activities. Entry of Journals and review and posting to ledgers are the two core bookkeeping activities. The journals are where all transactions are first recorded on a daily basis. Information from a journal is then posted to the ledgers to update each account. Various accounts in the ledgers are then summarized, tested, and validated, and used for producing financial statements at the end of an accounting period.
Here we will help you understand the basic accounting concepts and expose you to the general ledger process of entry of journals, review, posting summarization, reconciliation and finally reporting and closing of an accounting period. This section from TechnoFunc will help you understand the fundamentals of an effective automated general ledger system and subsequently explain all the important GL concepts including how to analyze a transaction, record it in the appropriate journal, and then post it to the ledgers. We assure you this is the best place to learn the record to report process!!
Concept of Legal Entity
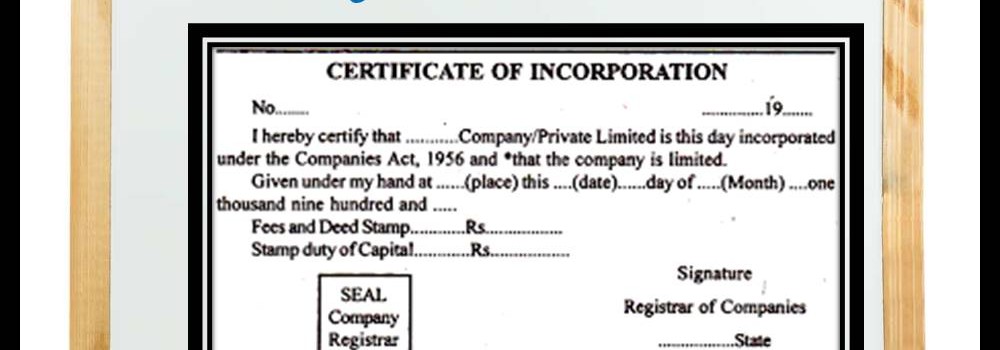
A legal entity is an artificial person having separate legal standing in the eyes of law. A Legal entity represents a legal company for which you prepare fiscal or tax reports. A legal entity is any company or organization that has legal rights and responsibilities, including tax filings.
Operational Structures in Business
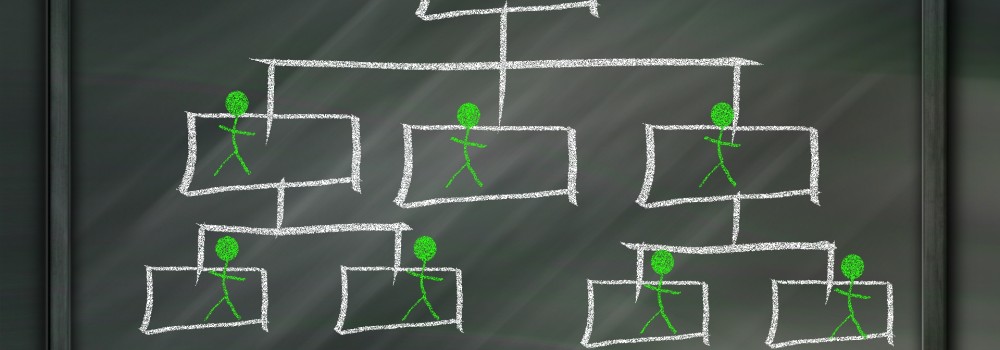
Large organizations grow through subsidiaries, joint ventures, multiple divisions and departments along with mergers and acquisitions. Leaders of these organizations typically want to analyze the business based on operational structures such as industries, functions, consumers, or product lines.
Horizontal or Flat Organizational Structures
Flat organizational structure is an organizational model with relatively few or no levels of middle management between the executives and the frontline employees. Its goal is to have as little hierarchy as possible between management and staff level employees. In a flat organizational structure, employees have increased involvement in the decision-making process.
Hierarchical Organization Structures
Hierarchical structure is typical for larger businesses and organizations. It relies on having different levels of authority with a chain of command connecting multiple management levels within the organization. The decision-making process is typically formal and flows from the top down.
Functional Organizational Structures

A functional organizational structure is a structure that consists of activities such as coordination, supervision and task allocation. The organizational structure determines how the organization performs or operates. The term organizational structure refers to how the people in an organization are grouped and to whom they report.
Divisional Organizational Structures

The divisional structure or product structure consists of self-contained divisions. A division is a collection of functions which produce a product. It also utilizes a plan to compete and operate as a separate business or profit center. Divisional structure is based on external or internal parameters like product /customer segment/ geographical location etc.
Matrix Organizational Structures

In recent times the two types of organization structures which have evolved are the matrix organization and the network organization. Rigid departmentalization is being complemented by the use of teams that cross over traditional departmental lines.
Shared Services Model

Shared Services is the centralization of service offering at one part of an organization or group sharing funding and resourcing. The providing department effectively becomes an internal service provider. The key is the idea of 'sharing' within an organization or group.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved