- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Equity and Liability Accounts
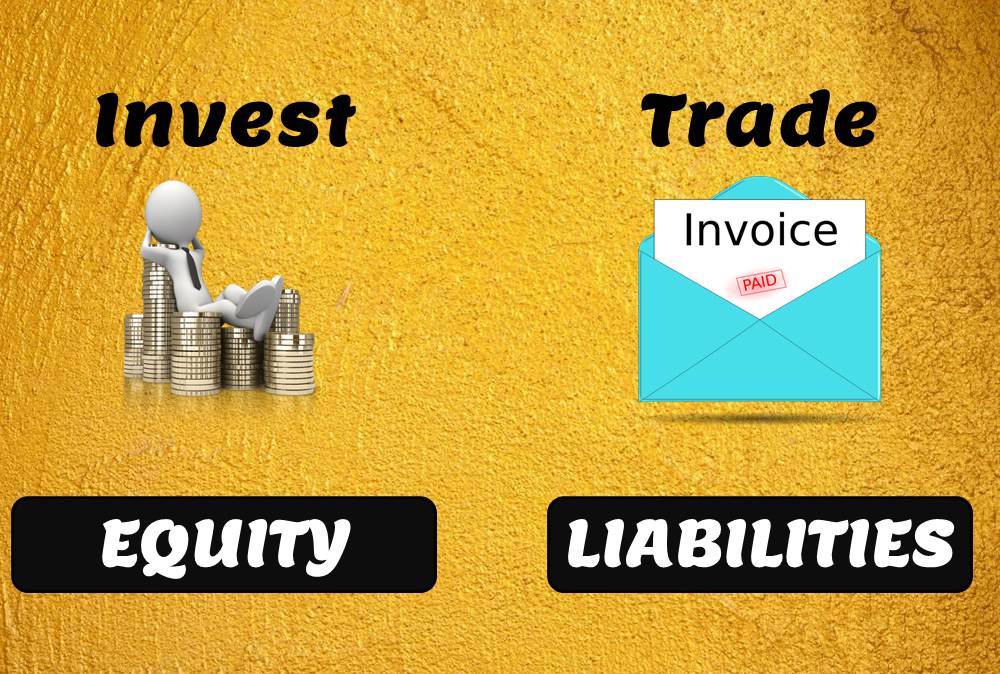
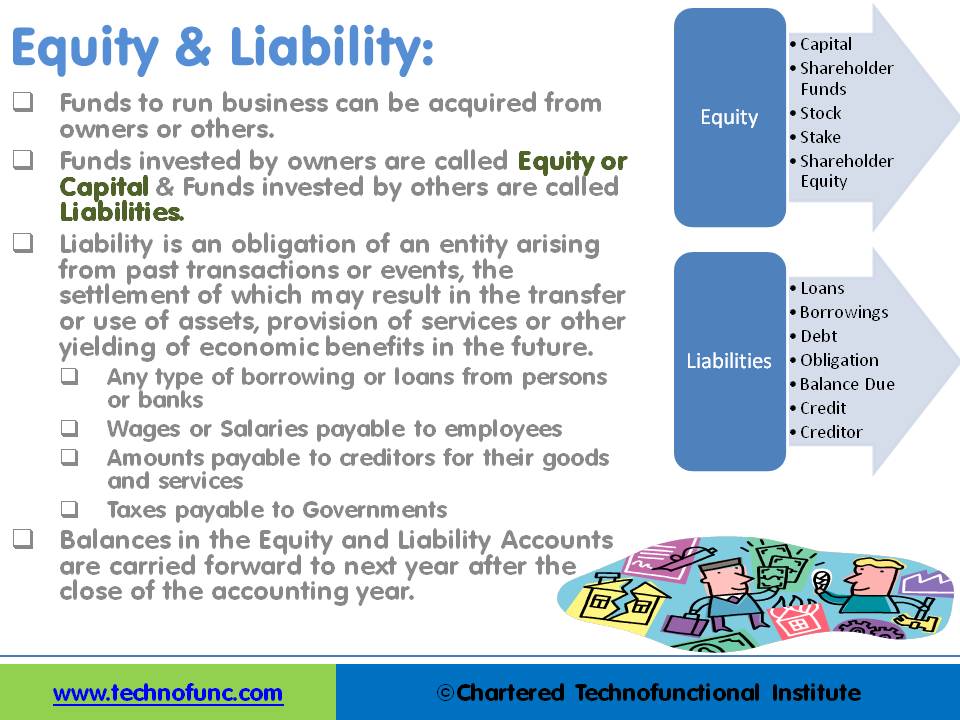
Equity and Liability Accounts
Funds contributed by owners in any business are different from all other types of funds. Equity is the residual value of the business enterprise that belongs to the owners or shareholders. The funds contributed by outsiders other than owners that are payable to them in the future. Liabilities are generally classified as Short Term (Current) and Long Term Liabilities. Current liabilities are debts payable within one year.
Equity Accounts:
The amount of the funds contributed by the owners (the stockholders) added or subtracted by accumulated gains and losses. Equity is the residual value of the business enterprise that belongs to the owners or shareholders.
Funds contributed by owners in any business are different from all other types of funds. Generally, they don’t have any cost of carrying for the business and in the event of winding up of the business, shareholders are entitled to the residual value of the business after discharging all other liabilities. They are expected to remain invested in the business for a long period of time and no immediate payback is anticipated in case of a going concern.
Equity accounts are also referred to as “Capital Account”, “Shareholder’s Funds” or “Accounts”, “Stock, Stake” and “Shareholder Equity”. Normally they have a credit balance and are reflected on the left side of the balance sheet. Profits and losses from each accounting year are added to Equity at the end of each year.
Balances in the Retained Earnings Account are transferred to “Equity” at the end of each accounting year. While running a revaluation of balances, equity is revalued using the historical rates in accordance with the accounting standards. Equity is a separate account type in ERP’s to segregate funds from owners and others.
Liability Accounts:
The number of funds contributed by outsiders other than owners that are payable to them in the future. Liability is an obligation of an entity arising from past transactions or events, the settlement of which may result in the transfer or use of assets, provision of services, or another yielding of economic benefits in the future.
Liabilities are generally classified as Short Term (Current) and Long Term Liabilities. Current liabilities are debts payable within one year, while long-term liabilities are debts payable over a longer period.
Liabilities can be from a lot of sources like Loans, External Borrowings, Debt – Secured and Unsecured, Obligation for services received Balance Due or Credit due to Creditors. Some generally known examples of liabilities are any type of borrowing or loans from persons or banks or wages or salaries paid to employees or amounts payable to creditors for their goods and services and taxes payable to Governments.
Balances in the Equity and Liability Accounts are carried forward to next year after the close of the accounting year. While running a revaluation of balances, liability is revalued using the period end rates in accordance with the accounting standards. Liability is a separate account type in ERP’s to segregate funds from owners and others.
Intercompany transactions also result in receivables and liabilities (payables) between different units of the same entity. Such transactions are settled in cash if they are in the normal course of business. At the time of the final consolidation of accounts, these intercompany liabilities and assets need to be eliminated from the books of the parent entity. We will discuss this concept in detail in the Intercompany chapter.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
The purpose of the general ledger is to sort transaction information into meaningful categories and charts of accounts. The general ledger sorts information from the general journal and converts them into account balances and this process converts data into information, necessary to prepare financial statements. This article explains what a general ledger is and some of its major functionalities.
-
In this article, we will explain the general Ledger journal processing flow from entering journals to running the final financial reports. Understand the generic general ledger process flow as it happens in automated ERP systems. The accounting cycle explains the flow of converting raw accounting data to financial information whereas general ledger process flow explains how journals flow in the system.
-
This article explains the process of entering and importing general ledger journals in automated accounting systems. Learn about the basic validations that must happen before the accounting data can be imported from any internal or external sub-system to the general ledger. Finally, understand what we mean by importing in detail or in summary.
-
Internally, an organization can be structured in many different ways, depending on their objectives. The internal structure of an organization will determine the modes in which it operates and performs. Organizational structure allows the expressed allocation of responsibilities for different functions and processes to different entities such as the branch, department, workgroup and individual.
-
Understand what we mean by GAAP to STAT adjustments. This article discusses the different standards that are used for multiple representations of the financial results for global organizations. Understand the meaning of US GAAP, Local GAAP, STAT, IFRS, and STAT. Finally, understand why accounting differences arise and how they are adjusted for different financial representations.
-
A Company (also called corporation) may be understood as an association of persons in which money is contributed by them, to carry on some business or undertaking. Persons who contribute the money are called the shareholders or the members of the company. A corporation is an artificial being, invisible, intangible and existing only in contemplation of law. Being the mere creature of law, it possesses only those properties which the charter of its creation confers upon it.
-
Functional Organizational Structures
A functional organizational structure is a structure that consists of activities such as coordination, supervision and task allocation. The organizational structure determines how the organization performs or operates. The term organizational structure refers to how the people in an organization are grouped and to whom they report.
-
Shared Services is the centralization of service offering at one part of an organization or group sharing funding and resourcing. The providing department effectively becomes an internal service provider. The key is the idea of 'sharing' within an organization or group.
-
An account inquiry is a review of any type of financial account, whether it be a depository account or a credit account. In this tutorial, you learn what we mean by drill through functionality in the context of the general ledger system. We will explain the concept of drill-down and how it enables users to perform account and transaction inquiry at a granular level and the benefits of using this functionality.
-
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles define the accounting procedures, and understanding them is essential to producing accurate and meaningful records. In this article we emphasize on accounting principles and concepts so that the learner can understand the “why” of accounting which will help you gain an understanding of the full significance of accounting.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved