- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Business Processes
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- GAAP to STAT Adjustments
GAAP to STAT Adjustments
Understand what we mean by GAAP to STAT adjustments. This article discusses the different standards that are used for multiple representations of the financial results for global organizations. Understand the meaning of US GAAP, Local GAAP, STAT, IFRS, and STAT. Finally, understand why accounting differences arise and how they are adjusted for different financial representations.
Why do we have different Standards?
All companies keep track of their financial results through accounting using the general ledger. However, during the process, there are several different methods of accounting that these companies can use, and usage of these methods can result in different accounting treatments for the same transaction. Cash and Accrual are two fundamental accounting methods.
Leveraging the fundamental principles of accounting, different bodies prescribe some standards that need to be followed by organizations coming under their authority. The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) is the authoritative body having the primary responsibility for developing accounting principles. The FASB publishes Statements of Financial Accounting Standards as well as Interpretations of these Standards.
Apart from “Financial Accounting Standards Board” (FASB), the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA), and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) along with the statutory authoritative bodies of various countries (Example – Institute of Chartered Accountants of India, for India), all have all played an influential role in developing generally accepted accounting principles which span across boundaries of nation and have global acceptability. Efforts are still going on to emerge globally accepted principles, as we still found variations in principles from countries to countries as well as from businesses to businesses that warrant a need to have different accounting methods.
Companies following under the jurisdiction of different geographies may have to follow standards prescribed by different bodies. For example, all companies that are registered in the United States of America need to follow US GAAP, and if, these counties are operating in different countries, they need to follow the accounting standards prescribed by the governments of that particular country for the legal entities registered in these foreign countries.
What are these Standards?
Two of the most common accounting methods that businesses employ are the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles and the STAT (Local Statutory Accounting Principles). To convert from one standard to another method, a business must make certain adjustments to its financial statements. Given below are some of the commonly used standards:
- US GAAP (the US Generally Accepted Accounting Principles)
- Local GAAP (Local Generally Accepted Accounting Principles)
- IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards)
- Tax Standards & Other Industry Specific Standards
- STAT (Local Statutory Accounting Principles)
- SAP (Statutory Accounting Principles)
Method 1: What is USGAAP?
In the U.S., Generally Accepted Accounting Principles are accounting rules used to prepare, present, and report financial statements for a wide variety of entities, including publicly traded and privately held companies, non-profit organizations, and governments. The term is usually confined to the United States; hence it is commonly abbreviated as US GAAP.
US GAAP is not written in the law, although the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) requires that it be followed in financial reporting by all publicly traded companies. The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) is the highest authority in establishing generally accepted accounting principles for public and private companies, as well as non-profit entities. All companies registered with US SEC have to comply and present their financial statements as per USGAAP.
Method 2: What is Local GAAP?
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles encompass the entire industry of accounting and not only the United States. As US Government has notified standards for US companies, similarly most of the countries have established and notified accounting standards and principles that need to be adhered to and complied with all organizations operating within the jurisdiction of respective countries. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) refer to the standard framework of guidelines for financial accounting used in any given jurisdiction; generally known as accounting standards. Local GAAP includes the standards, conventions, and rules accountants follow in recording and summarizing, and in the preparation of financial statements, where the word local refers to and can be replaced by the respective authority or jurisdiction. For example - A US company operating in other countries needs to comply with respective Local GAAPs for operations in respective countries and need to report its consolidated results in US GAAP.
Method 3: What is IFRS?
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are principles-based standards, interpretations, and the framework adopted by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). They are also known by the older name of International Accounting Standards (IAS) and they aim for international accounting standards that can be adopted by all organizations worldwide.
Among other standards, IFRS is best positioned to be a global standard. Local and US GAAPs are slowly being phased out in favor of the International Financial Reporting Standards as the global business becomes more pervasive. US GAAP applies only to United States financial reporting and thus an American company reporting under US GAAP might show different results if it was compared to a British company that uses the International Standards or Local UK GAAP. While there is a tremendous similarity between GAAP and the international rules, the differences can lead a financial statement user to incorrectly believe that company A made more money than company B simply because they report using different rules. The move towards International Standards seeks to eliminate this kind of disparity. At present, IFRS is used in many parts of the world, including the European Union, India, Hong Kong, Australia, Malaysia, Pakistan, GCC countries, Russia, South Africa, Singapore, and Turkey. As of August 2008, more than 113 countries around the world require or permit IFRS reporting. It is generally expected that IFRS adoption worldwide will be beneficial to investors and other users of financial statements, by reducing the costs of comparing alternative investments and increasing the quality of information. However, this requires a big-picture strategic approach that ensures global consistency in financial reporting policies and practices.
Method 4: What are Tax Standards & Other Industry Specific Standards?
Many governments prescribe different accounting standards for companies operating in a particular domain. For example, US SAP is a set of accounting standards and procedures that insurance companies use to report their financial data. US GAAP and US SAP procedures differ considerably. State insurance regulators require insurance companies to keep their accounting records for filing annual financial reports in accordance with statutory accounting principles (SAP) and the Statutory Accounting Principles (SAP) forms the basis for preparing the financial statements of insurance companies. As the US insurance industry falls under state regulation, actual rules vary further by state. Similarly, tax laws for various countries may prescribe different accounting treatments in certain cases that do not match even with the respective Local GAAPs.
Method 5: What is the STAT (Local Statutory Accounting Principles)?
Today organizations are more global than ever and they operate across boundaries of nations. GAAP and STAT in this context are terms used to define how the results of a multinational corporation will be recorded and reported for different purposes. In the context of general ledger, GAAP generally refers to the GAAP prescribed by the home country where the organization’s parent company is registered and has an obligation to report the consolidated results. The STAT term is generally used to refer to the local statutory books of accounts to reflect the operations in a specific foreign country for operations in that country as per the Local GAAP for that specific country.
What is GAAP to STAT adjustments?
As companies need to report results from the same business operations using different accounting standards, they need to make adjustments to their recorded financial data, to convert the financial information recorded using one accounting method to another. These adjustments entries are in the nature of permanent adjustments, timing adjustments, reclassifications, or eliminations.
- Under Local GAAP accounting, payments for goods or services may be recorded as expenses however for US GAAP (full accrual basis) accounting, payments made in this fiscal year for goods and services that won’t be used until after the end of the year represent purchases of assets, not expenses and GAAP adjustment is required for the portion of the goods or services that will be used in future years. This is an example of GAAP to STAT adjustment arising out of a timing difference.
- SAP applicable for insurance companies operates on different accounting principles to provide information that is useful under different industry-specific circumstances. For example, SAP guidelines are used to prepare financial statements that allow investors to determine the ability of the insurance company to pay their future claims. In other words, if all customers of the insurance company had a claim at present, SAP helps to determine if the company would be able to pay those insurance claims. On the other hand, US GAAP guidelines treat a business as a going concern, and therefore, the focus is on preparing the financial statements by matching revenues with expenses, so an investor can gauge the underlying profitability of the business for the current year.
- Various tax laws applicable in various countries prescribe different rules for the treatment of assets for accounting purposes. The depreciation rules are different and there are differences in the way the residual value can be considered. While most assets have at least some value under GAAP, some assets might not have any value under the TAX method.
How to make GAP to STAT adjustments:
To adjust a balance sheet from one accounting method to another (for example GAAP to STAT), an accountant must identify and adjust the accounting entries that would require a different treatment. From an accounting perspective, there are three distinct stages for this adjustment process, assess individual situation and requirements, complete the conversion activities, and sustain ongoing reporting. Organizations need to develop a framework and systems design for accounting, reporting, consolidation, and reconciliation processes and controls. Modern general ledger systems enable accountants to organize and record accounting data by providing an operating model for multiple financial representations.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Reversing Journals are special journals that are automatically reversed after a specified date. A reversing entry is a journal entry to “undo” an adjusting entry. When you create a reversing journal entry it nullifies the accounting impact of the original entry. Reversing entries make it easier to record subsequent transactions by eliminating the need for certain compound entries. See an example of reversing journal entry!
-
GL - Review & Approve Journals
Review and Approval mechanisms ensure that the accounting transaction is reasonable, necessary, and comply with applicable policies. Understand why we need review and approval processes, what are they, and how they are performed in automated general ledger systems. Learn the benefits of having journal approval mechanisms in place.
-
Internally, an organization can be structured in many different ways, depending on their objectives. The internal structure of an organization will determine the modes in which it operates and performs. Organizational structure allows the expressed allocation of responsibilities for different functions and processes to different entities such as the branch, department, workgroup and individual.
-
Five Core General Ledger Accounts
Typically, the accounts of the general ledger are sorted into five categories within a chart of accounts. Double-entry accounting uses five and only five account types to record all the transactions that can possibly be recorded in any accounting system. These five accounts are the basis for any accounting system, whether it is a manual or an automated accounting system. These five categories are assets, liabilities, owner's equity, revenue, and expenses.
-
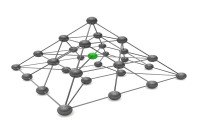
Network Organizational Structures
The newest, and most divergent, team structure is commonly known as a Network Structure (also called "lean" structure) has central, core functions that operate the strategic business. It outsources or subcontracts non-core functions. When an organization needs to control other organizations or agencies whose participation is essential to the success, a network structure is organized.
-
Multitude of these legal and operational structures clubbed with accounting and reporting needs give rise to many reporting dimensions at which the organization may want to track or report its operational metrics and financial results. This is where business dimensions play a vital role.
-
Concept of Representative Office
A representative office is the easiest option for a company planning to start its operations in a foreign country. The company need not incorporate a separate legal entity nor trigger corporate income tax, as long as the activities are limited in nature.
-
What is a Business Eco System?
The goal of a business is to generate capital appreciation and profits for its owners or stakeholders by engaging in provision of goods and services to customers within the eco system/framework governed by respective laws(local/international). The eco system involves various entities that the business works with for delivery of a product or service.
-
An allocation is a process of shifting overhead costs to cost objects, using a rational basis of allotment. Understand what is the meaning of allocation in the accounting context and how defining mass allocations simplifies the process of allocating overheads to various accounting segments. Explore types of allocations and see some practical examples of mass allocations in real business situations.
-
Horizontal or Flat Organizational Structures
Flat organizational structure is an organizational model with relatively few or no levels of middle management between the executives and the frontline employees. Its goal is to have as little hierarchy as possible between management and staff level employees. In a flat organizational structure, employees have increased involvement in the decision-making process.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved