- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Defining Internal Structures
Defining Internal Structures
Internally, an organization can be structured in many different ways, depending on their objectives. The internal structure of an organization will determine the modes in which it operates and performs. Organizational structure allows the expressed allocation of responsibilities for different functions and processes to different entities such as the branch, department, workgroup and individual.
Internally, an organization can be structured in many different ways, depending on their objectives. The internal structure of an organization will determine the modes in which it operates and performs. Organizational structure allows the expressed allocation of responsibilities for different functions and processes to different entities such as the branch, department, workgroup and individual.
We know that big multinational organizations operate in a matrix environment, constitute of many units and need different views of their operating and financial results. These different views may represent financials or profitability by geographies, countries, locations, businesses, segments, product lines, cost centers, functions, COE’s etc.
Various types of operational units, functional units and divisional units widely used across industry are briefly explained below:
|
Dimension |
Explanation |
|
Cost centers |
A cost center is part of an organization that does not produce direct profit and adds to the cost of running a company. Examples of cost centers include marketing & finance departments. It is an operating unit in which managers are accountable for budgeted and actual expenditures. Used for the management and operational control of business processes that may span legal entities. |
|
Business units/ Management Entity |
A semi-autonomous operating unit that is created to meet strategic business objectives. Used for financial reporting that is based on industries or product lines that the organization serves independently of legal entities. |
|
Value streams |
An operating unit that controls one or more production flows. Commonly used in lean manufacturing to control the activities and flows that is required to supply a product or service to consumers. |
|
Business Functions/ Departments / Divisions |
A department or division can be viewed as the intersection between a legal entity and a business unit. Departments can serve as profit centers. They can be used as cost accumulators and for revenue recognition. They may have profit and loss responsibility, and may consist of a group of cost centers. This operating unit defines academic areas, research units, or administrative offices with an appointed manager, that have programmatic, operational, fiscal and/or budgetary responsibility for a specific set of activities and projects/grants. |
|
Retail channels |
An operating unit that represents a brick and mortar store, an online store or an online marketplace. Used for the management and operational control of one or more stores within or across legal entities. |
|
Business Support Functions |
An operating unit that represents a category or functional part of an organization that performs a specific task to support inward-directed activity, such as sales or marketing to support business. Used to report on functional areas. A support function may have allocated budgets and may consist of a group of cost centers. |
|
Organization Support Functions |
Self-directed activity systems of an organization concerned with establishing and maintaining the organization as an entity. Each organization support function provides support to all functions, business, business support and other organization support functions. For example, corporate finance, IT functions, administration and knowledge management. An organization support function may have allocated budgets and may consist of a group of cost centers. |
|
Profit Center |
A profit center is a part of a corporation that directly adds to its profit, treated as a separate business and for which the profits or losses are calculated separately. This operating unit is held accountable for both revenues, and costs (expenses), and therefore, profits. Different profit centers are separated for accounting purposes so that the management can measure their relative efficiency and profit. |
|
Business Locations/ Countries/ Geography/ Supplier & Customer Locations |
Organizations operate from more than one location and may need to track where a particular financial transaction occurred. Some examples of need to track different locations could be transactions through sales offices, factories, subsidiaries etc. Organizations may even need to analyze the financial information based on the supplier’s or customer’s location may require a location segment dedicated to this. However this has very limited application in terms of usefulness. E.g. software companies cater to clients from all over the world & may like to make strategies based on which customer territory contributed how much to the revenue & hence a customer location is an important segment but for a manufacturing organization this will hold no relevance. |
|
Project Area
|
Certain organizations have their business models build around project activities. E.g. a property developer may like to have all its cost & revenue against individual projects. These organizations may have multiple projects running under same legal entity. There projects have their own budget & statutory requirements & hence their own trial balance. |
|
Product Lines/Service Lines
|
Some organizations deal in products which are low in volume but high in value. These organizations would like to analyze their costs & revenue for individual products. They also need to apportion indirect costs & revenues to these products/services so that the financials provide a full picture on product performance. On the other hand, a supermarket dealing in thousands of product might not have any interest in recording every transaction against the individual product or track financials at product level. Further each legal entity in the group may have its own set of released products that it wants to include in transaction documents. |
|
Accounts/Sub Accounts
|
Natural Accounts captures the nature of financial transactions such as Assets, Liabilities, Fund Equity, Revenues, and Expenditures. It captures the transactional information at detailed level that can be summarized to parent accounts for external and internal company-wide reporting. This hierarchy is helpful in organizing and summarizing reports. |
|
Business Employee Hierarchy |
Business employee hierarchy is the pyramidal type arrangement of the organizational employees. This vertical hierarchy helps in delegation of authority based on the span of control at multiple levels of employees. Each level in the hierarchy becomes an integral part of the chain of command and acts as the channel for transmission of authority to the succeeding lower level of the management. These hierarchical structures in organizations narrow down as we move in the upward direction and showcase centralization in the whole setup. At transactional level it is used to define the authority and set approval path and limits. |
|
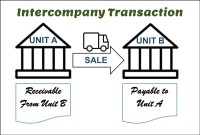
Elimination Entity |
When a parent company does business with one or more subsidiary companies and uses consolidated financial reporting, any transactions between the companies must be removed, or eliminated, from the financial reports. These transactions are called elimination transactions. The destination company for eliminations is called the elimination company. |
|
Consolidation Entity |
A legal entity which is the consolidation company. During consolidation, transactions from several company accounts of subsidiaries is aggregated into a single company |
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
For any company that has a large number of transactions, putting all the details in the general ledger is not feasible. Hence it needs to be supported by one or more subsidiary ledgers that provide details for accounts in the general ledger. Understand the concept of the subsidiary ledgers and control accounts.
-
After reading this article the learner should be able to understand the meaning of intercompany and different types of intercompany transactions that can occur. Understand why intercompany transactions are addressed when preparing consolidated financial statements, differentiate between upstream and downstream intercompany transactions, and understand the concept of intercompany reconciliations.
-
Introduction to Legal Entities Concept
Modern business organizations operate globally and leverage a large number of registered legal entities, and operate through complex matrix relationships. To stay competitive in the current global business environment, they must often develop highly diverse and complex organizational structures that cross international borders. Learn more about Legal Entities and their importance for businesses.
-
Operational Structures in Business
Large organizations grow through subsidiaries, joint ventures, multiple divisions and departments along with mergers and acquisitions. Leaders of these organizations typically want to analyze the business based on operational structures such as industries, functions, consumers, or product lines.
-
There are five types of core accounts to capture any accounting transaction. Apart from these fundamental accounts, some other special-purpose accounts are used to ensure the integrity of financial transactions. Some examples of such accounts are clearing accounts, suspense accounts, contra accounts, and intercompany accounts. Understand the importance and usage of these accounts.
-
Concept of Representative Office
A representative office is the easiest option for a company planning to start its operations in a foreign country. The company need not incorporate a separate legal entity nor trigger corporate income tax, as long as the activities are limited in nature.
-
Explore the concept of journal reversals and understand the business scenarios in which users may need to reverse the accounting entries that have been already entered into the system. Understand the common sources of errors resulting in the reversal of entries and learn how to correct them. Discuss the reversal of adjustment entries and the reversal functionalities in ERPs.
-
Shared Services is the centralization of service offering at one part of an organization or group sharing funding and resourcing. The providing department effectively becomes an internal service provider. The key is the idea of 'sharing' within an organization or group.
-
As the business grows, the company may want to transition to a branch structure as branches are allowed to conduct a much broader range of activity than representative offices. Branches can buy and sell goods, sign contracts, build things, render services, and generally everything that a regular business can do. A company expands its business by opening up its branch offices in various parts of the country as well as in other countries.
-
GL - Unearned / Deferred Revenue
Unearned revenue is a liability to the entity until the revenue is earned. Learn the concept of unearned revenue, also known as deferred revenue. Gain an understanding of business scenarios in which organizations need to park their receipts as unearned. Look at some real-life examples and understand the accounting treatment for unearned revenue. Finally, look at how the concept is treated in the ERPs or automated systems.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved