- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- GL - Journal Entry & Import
GL - Journal Entry & Import
This article explains the process of entering and importing general ledger journals in automated accounting systems. Learn about the basic validations that must happen before the accounting data can be imported from any internal or external sub-system to the general ledger. Finally, understand what we mean by importing in detail or in summary.
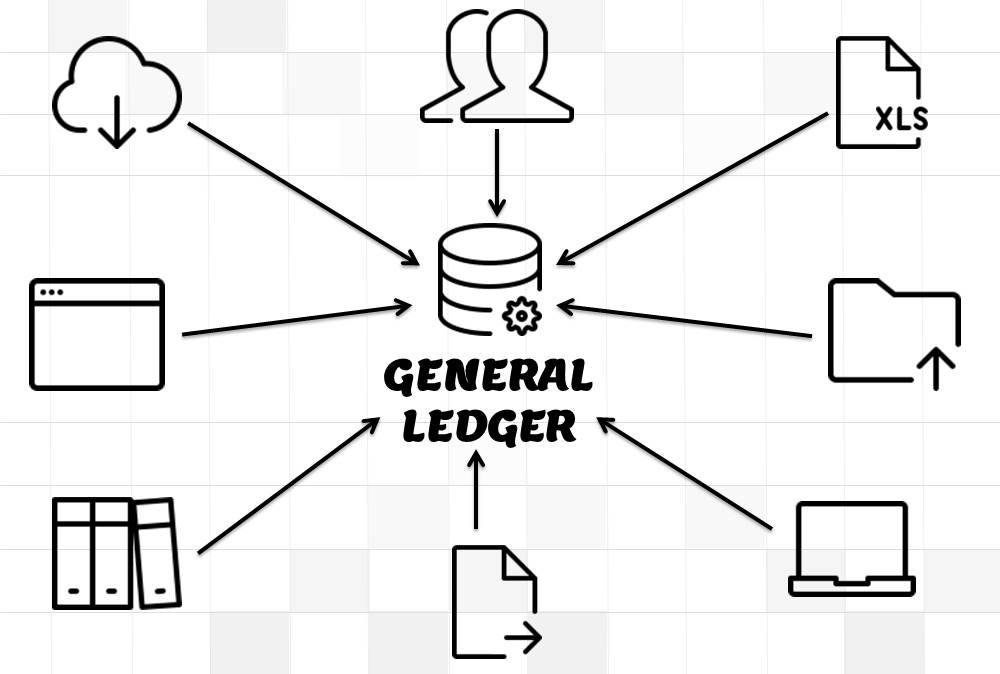
Recording Journals in General Ledger:
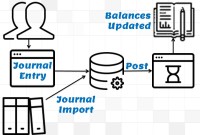
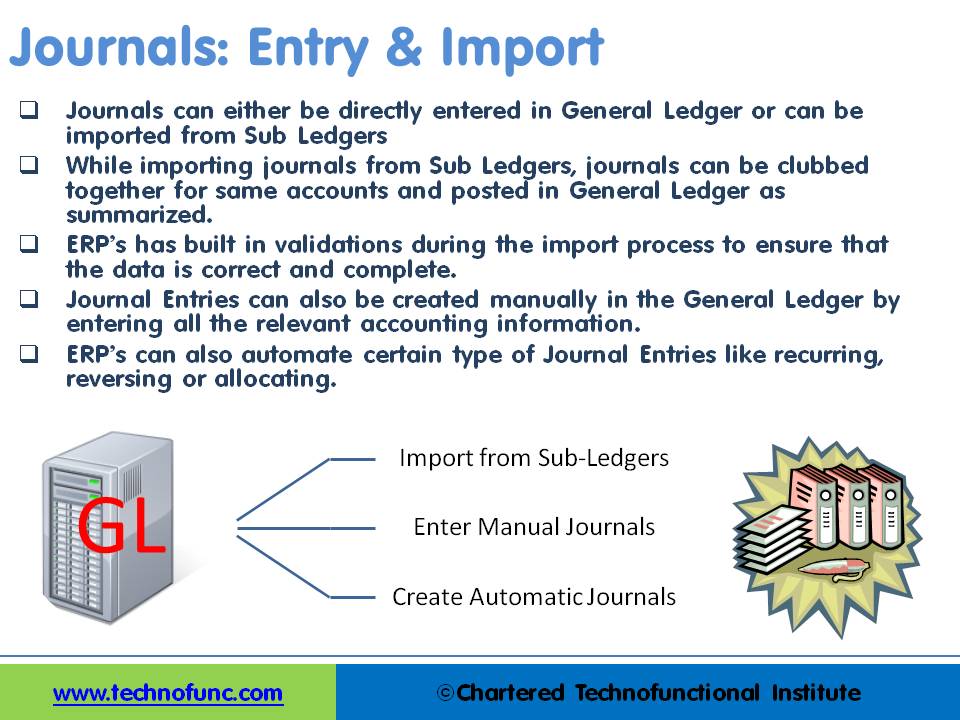
Journals can either be directly entered in General Ledger or can be imported from Sub Ledgers. Most of the journals are created along-with business transactions like sales, purchases, receipts, and payments and get recorded in respective sub-ledgers. As sub-ledgers generally capture data at a more granular level, the relevant accounting information must flow to the general ledger for posting and subsequent reporting. From sub-ledgers, they need to be imported to the general ledger for financial recording and reporting.
Journal Entries can also be created manually in General Ledger by entering all the relevant accounting information. ERPs can also automate certain types of Journal Entries like recurring, reversing, or allocating journals. In case of manual entry follow the steps and guidelines outlined in the Recording Journals tutorial.
Importing – Detail V/s Summarized:
While importing journals from Sub Ledgers, journals can be clubbed together for the same accounts and posted in General Ledger as summarized.
Various general ledger systems provide the functionality to create Summary Journals which summarize all transactions for the same account, period, and currency into one debit or credit journal line. This results in fewer transactions in the general ledger systems and makes financial reports more manageable in size. In the case of summary journal users, lose the one-to-one mapping of detail transactions in the sub-ledger to the summary journal lines created by the import process. However most of the organizations use this feature as this prevents too many transactions in GL Accounts and transactions get clubbed based on category, type, or transaction source.
Using the drill-down functionalities available in most of the modern general ledger systems, users can still perform various review and analysis functions, as even if the system creates summary journals, it can still maintain a mapping of how Journal Import summarizes sub-ledger detail transactions from feeder systems into general ledger journal lines.
Journal Import Validations:
ERP’s and automated accounting systems must have built in validations during the import process to ensure that the data is correct and complete. An effective Journal Import program should validate key accounting information before it creates journal entries in the General Ledger application to prevent errors and reconciliation efforts.
Given below are some of the common data validations that can happen during the GL Import process:
1. Suspense Posting:
Suspense posting puts the remaining amount in the suspense account in case the debits and credits of the journal are not matching. In case it is not required, Journal Import should reject all invalid lines that do not balance.
2. Duplicate Batch Name:
If the batch name is a unique field then Journal Import should ensure that a batch with the same name does not already exist for the same period in the General Ledger application. Similarly, it must also check to ensure that more than one journal entry with the same name does not exist for a batch.
3. Other Attributes:
Attributes that can be validated to ensure that journals contain the appropriate accounting data could be accounting books, period, source, currency, category, accounting date, reversal period, account validation, account code combinations, effective date, roll date, and any other required validations.
Import Using Excel:
In today’s accounting world, financial and operational data typically is stored in a variety of programs and formats. Excel is one of such tools, most widely used by the accountants! When accountants need to prepare a report based on data from various systems, the first step is to export the data into Excel. Many times accounting information is stored in chronological order in excels by the accountants, and examples include adjusting entries and recurring entries.
Benefits of using the excel upload feature are that it makes life much easier for data operator and accounts executives. The great flexibility of excel based application increases productivity and results in reduced training costs as most users are already familiar with the excel functionalities and also improves user acceptance for automated systems. The biggest benefit comes from the fact that excel upload can also work in disconnected environments.
Typically, most of the automated systems provide the functionality to import accounting data from Excel to the general ledger and create journals. Most ERPs provide the ability to upload journals using the MS Excel worksheet. You can create journals in Excel Template and upload directly to General Ledger.
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
In most of the automated financial systems, you can define more than 12 accounting periods in a financial year. This article will explain the concept of the adjustment period and the benefits of having adjustment periods. Adjustment periods have their inherent challenges for the users of financial statements and there is a workaround for those who don’t want to use adjustment periods.
-
In every journal entry that is recorded, the debits and credits must be equal to ensure that the accounting equation is matched. In this article, we will focus on how to analyze and recorded transactional accounting information by applying the rule of credit and debit. We will also focus on some efficient methods of recording and analyzing transactions.
-
There are two commonly used methods of accounting - Cash Basis and the Accruals Basis. Understand the difference between accruals and reversals. Recap the earlier discussion we had on accruals and reversals and see the comparison between these two different but related accounting concepts. Understand how the action of accruing results in reversals subsequently in the accounting cycle.
-
Prepayments and Prepaid Expenses
Prepayments are the payment of a bill, operating expense, or non-operating expense that settle an account before it becomes due. Learn the concept of prepaid expenses. Understand the accounting treatment for prepaid expenses. Understand the concept by looking at some practical examples and finally learn the adjusting entry for these expenses.
-
GL - Review & Approve Journals
Review and Approval mechanisms ensure that the accounting transaction is reasonable, necessary, and comply with applicable policies. Understand why we need review and approval processes, what are they, and how they are performed in automated general ledger systems. Learn the benefits of having journal approval mechanisms in place.
-
General Ledger - Advanced Features
Modern automated general ledger systems provide detailed and powerful support for financial reporting and budgeting and can report against multiple legal entities from the single system. These systems offer many advanced functionalities right from journal capture to advanced reporting. This article will provide an overview of some advanced features available in today's General Ledgers.
-
GL - Journal Posting and Balances
In this tutorial, we will explain what we mean by the posting process and what are the major differences between the posting process in the manual accounting system compared to the automated accounting systems and ERPs. This article also explains how posting also happens in subsidiary ledgers and subsequently that information is again posted to the general ledger.
-
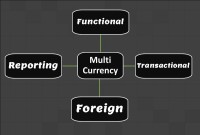
Multi Currency - Functional & Foriegn
Currency is the generally accepted form of money that is issued by a government and circulated within an economy. Accountants use different terms in the context of currency such as functional currency, accounting currency, foreign currency, and transactional currency. Are they the same or different and why we have so many terms? Read this article to learn currency concepts.
-
Although technically a general ledger appears to be fairly simple compared to other processes, in large organizations, the general ledger has to provide many functionalities and it becomes considerably large and complex. Modern business organizations are complex, run multiple products and service lines, leveraging a large number of registered legal entities, and have varied reporting needs.
-
A legal entity is an artificial person having separate legal standing in the eyes of law. A Legal entity represents a legal company for which you prepare fiscal or tax reports. A legal entity is any company or organization that has legal rights and responsibilities, including tax filings.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved