- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
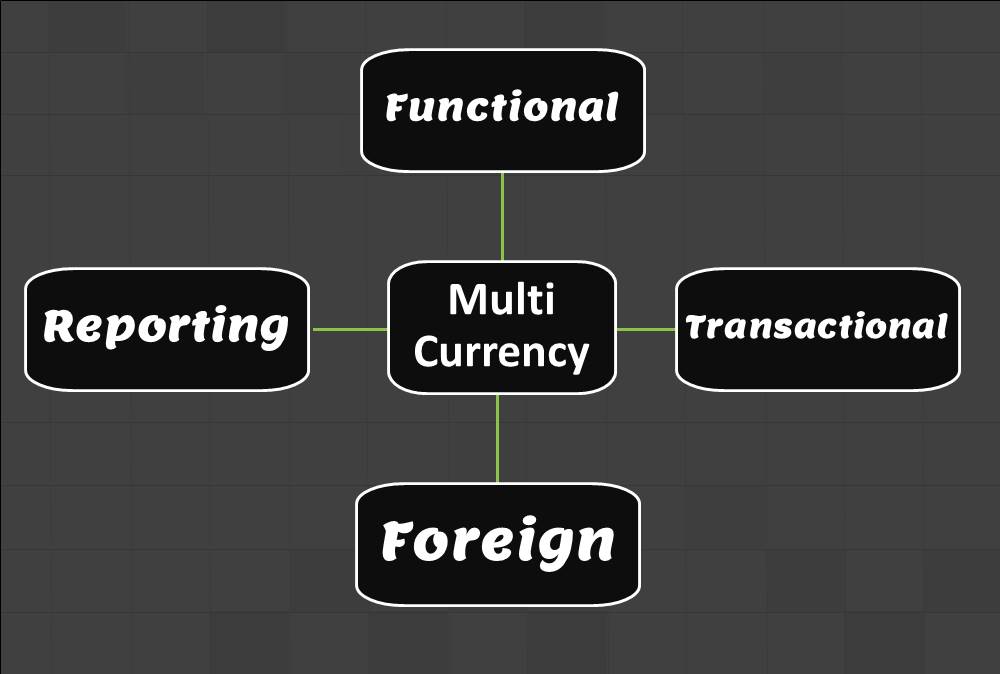
- Functional
- General Ledger (Record to Report)
- Concept of Foreign Branches
Concept of Foreign Branches
As the business grows, the company may want to transition to a branch structure as branches are allowed to conduct a much broader range of activity than representative offices. Branches can buy and sell goods, sign contracts, build things, render services, and generally everything that a regular business can do. A company expands its business by opening up its branch offices in various parts of the country as well as in other countries.
As the business grows, the company may want to transition to a branch structure as branches are allowed to conduct a much broader range of activity than representative offices. Branches can buy and sell goods, sign contracts, build things, render services, and generally everything that a regular business can do. A company expands its business by opening up its branch offices in various parts of the country as well as in other countries.
A branch office refers to an establishment which carries on substantially the same business and activity as is carried out by its Head Office. Foreign Branch of a company refers to the branch of a company that operates in the foreign country. It is a branch of a company operating outside the country of its registration.
Some attributes of foreign branch offices are:
- Does not require opening a separate legal entity in the country of operations
- The branch is legally part of the company and is not a separate entity
- The range of the activities that can be undertaken, substantially increase as compared to a representative office
- Branches generally a constitute taxable presence in a foreign country and must account for and file prescribed returns with the local authorities
- Attributing the profits to the branch activities require arm’s length transaction
- Foreign branch is subject to special tax considerations.
- A subsidiary of a foreign corporation generally is taxed as any other domestic corporation, that is, as a separate taxable entity apart from its foreign parent. In contrast, a branch of a foreign corporation is not treated as a separate taxable entity; instead, the code and regulations employ a set of special rules to determine the tax liability of the branch both in domestic country and foreign country of operations.
Such branch offices help the company in:
- Spreading its business to diverse locations and thus increasing the customer base
- Expanding the size of the market for a company's product by attracting more customers
- Bringing its product closer to the customers by increasing their accessibility to it
- Making the distribution and marketing of its goods and services easier and more effective
- Widening the scope of its trading and manufacturing activities
- Bringing more opportunities and opening unexplored avenues
- Fuel the growth of the company
- Enhance its profitability
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Driving Business Efficiency through Divisions and Departments
In case of a multi-divisional organizational structure, there is one parent company, or head-office. And that parent owns smaller departments, under the same brand name. Dividing the firm, into several self-contained, autonomous units, provides the optimal level of centralization, in a company.
-
Horizontal or Flat Organizational Structures
Flat organizational structure is an organizational model with relatively few or no levels of middle management between the executives and the frontline employees. Its goal is to have as little hierarchy as possible between management and staff level employees. In a flat organizational structure, employees have increased involvement in the decision-making process.
-
In some of the ERP tools, there are more than 12 accounting periods in a financial year. This article discusses the concept of accounting calendar and accounting periods. Learn why different companies have different accounting periods. Understand some of the commonly used periods across different organizations and the definition & use of an adjustment period.
-
General Ledger - Advanced Features
Modern automated general ledger systems provide detailed and powerful support for financial reporting and budgeting and can report against multiple legal entities from the single system. These systems offer many advanced functionalities right from journal capture to advanced reporting. This article will provide an overview of some advanced features available in today's General Ledgers.
-
A joint venture (JV) is a business agreement in which the parties agree to develop, for a finite time, a new entity and new assets by contributing equity. They exercise control over the enterprise and consequently share revenues, expenses and assets. A joint venture takes place when two or more parties come together to take on one project.
-
Reversing Journals are special journals that are automatically reversed after a specified date. A reversing entry is a journal entry to “undo” an adjusting entry. When you create a reversing journal entry it nullifies the accounting impact of the original entry. Reversing entries make it easier to record subsequent transactions by eliminating the need for certain compound entries. See an example of reversing journal entry!
-
Introduction to Legal Entities Concept
Modern business organizations operate globally and leverage a large number of registered legal entities, and operate through complex matrix relationships. To stay competitive in the current global business environment, they must often develop highly diverse and complex organizational structures that cross international borders. Learn more about Legal Entities and their importance for businesses.
-
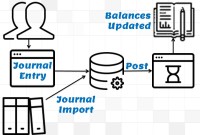
GL - Journal Posting and Balances
In this tutorial, we will explain what we mean by the posting process and what are the major differences between the posting process in the manual accounting system compared to the automated accounting systems and ERPs. This article also explains how posting also happens in subsidiary ledgers and subsequently that information is again posted to the general ledger.
-
GL - Different Type of Journals
Two basic types of journals exist: general and special. In this article, the learner will understand the meaning of journalizing and the steps required to create a journal entry. This article will also discuss the types of journals and will help you understand general journals & special journals. In the end, we will explain the impact of automated ERPs on the Journalizing Process.
-
Shared Services is the centralization of service offering at one part of an organization or group sharing funding and resourcing. The providing department effectively becomes an internal service provider. The key is the idea of 'sharing' within an organization or group.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved