- Home
- Business Processes
- Industry Knowledge
- Aerospace Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Banking Domain
- BFSI Industry
- Consumer/ FMCG Industry
- Chemicals Industry
- Engineering & Construction
- Energy Industry
- Education Domain
- Finance Domain
- Hospitality Domain
- Healthcare Industry
- Insurance Domain
- Retail Industry
- Travel and Tourism Domain
- Telecom Industry
- Leadership Skills
- eLearning
- Home
- Leadership
- Change Management
- Concept of Management
Concept of Management
The concept of management refers to the process of planning, organizing, staffing, directing, coordinating, and controlling to achieve organizational goals. It is the management of human, physical, financial, and other valuable resources of the organization in an effective and efficient manner to achieve business objectives.
Different people have conceived and defined management in different ways. But, the essence of management lies in determining worthwhile goals and then carefully selecting and utilizing resources through efficient and effective planning, organizing, actuating, and controlling to achieve those goals.
Who is a Manager?
You are a manager. What does this mean? The word derives from the ancient French word for handling horses and a later one for handling the affairs of the kitchen. Cynics might replace horses with donkey, but all would see the analogy of keeping an organization alive through the activities of the kitchen. Probably the one that is most simple, popular, and often quoted by many in general is "getting things done through other people."
Let us now look at different definitions that highlight important aspects of management.
- Management is a distinct process consisting of activities of planning, organizing, actuating and controlling, performed to determine and to accomplish stated objectives with the use of human beings and other resources (Martin, 1977).
- Good management is merely the exercise of common sense and the Golden Rule (Daniel, 1976)
- The six M’s (money, men, materials, methods, machines, and marketing) of management or the basic resources, as they are often called, are subjected to the fundamental functions of management - planning, organizing, actuating, and controlling -to achieve stated objectives.
- Management is an art struggling to become a science.
- Management science is a body of systematized knowledge accumulated and accepted with reference to the understanding of general truths concerning management.
- The art of management is a personal creative power plus skill in performance. The contemplation of problems, events, and possibilities develops personal creative power, while experience, observation, and study of results contribute to skilled performance. It other words, management art involves envisioning an orderly whole from chaotic parts, communicating the vision, and achieving the goal. It is the "art of arts" because it organizes and uses human talent (Boehringer, 1975)
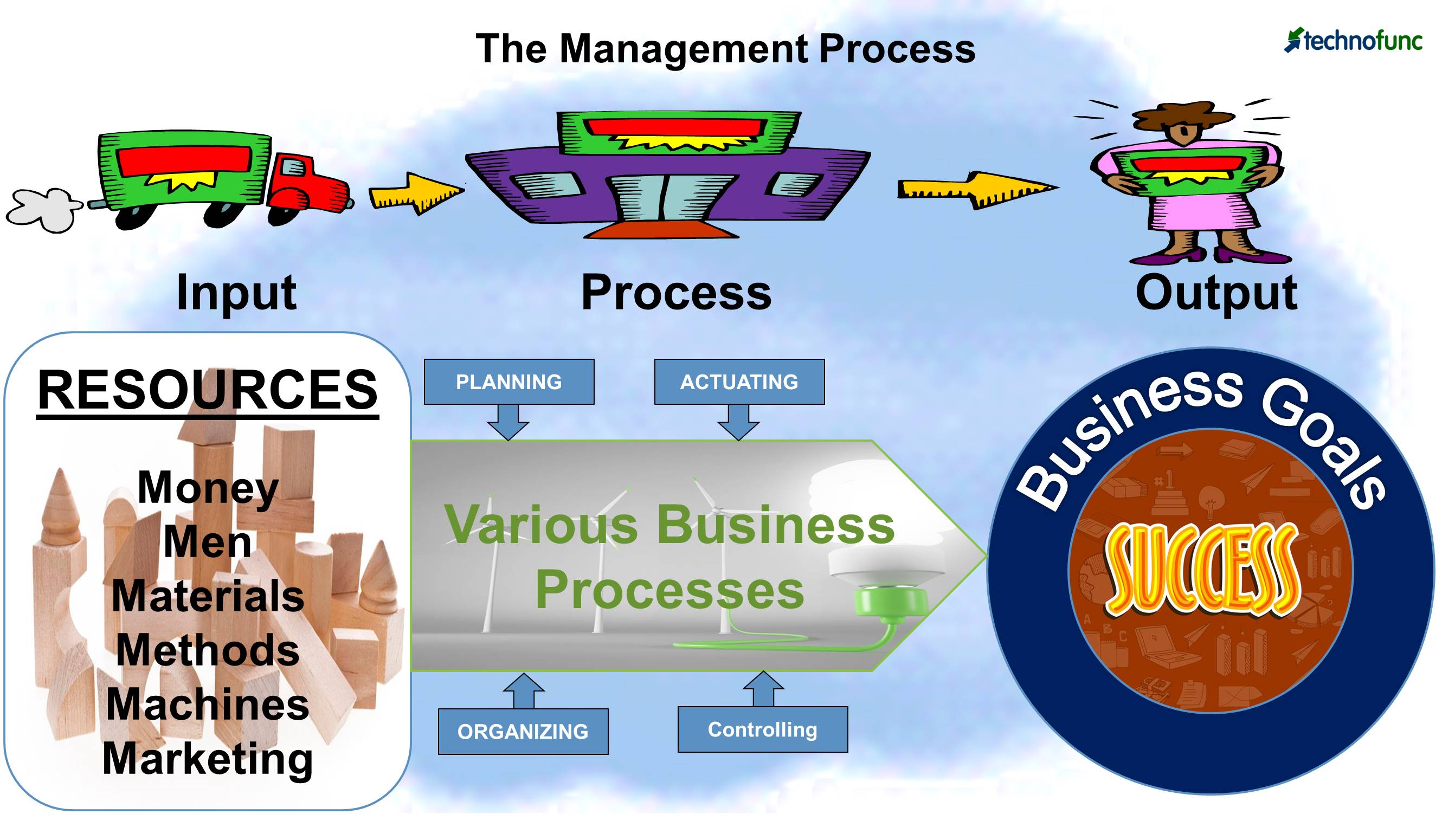
From these definitions, we can infer that the principles and the techniques of management are not only applicable to the business world but they can be equally applied universally. They also find application in social, religious, charitable, and non-profit organizational contexts.
Essentially we can conclude that management is the integration of human and other resources in a manner that leads to effective utilization and harmonization of the individual efforts with organizational goals.
Suggested Reading and Resources
Related Links
You May Also Like
-
Management theories are the recommended management strategies that enable us to better understand and approach management. Many management frameworks and guidelines were developed during the last four decades.
-
Management Principles by Fayol
Henri Fayol (1849-1925), a French industrialist and a prominent European management theorist, developed a general theory of management. Fayol outlined the fourteen principles of management.
-
Quantitative Theory of Management
The quantitative management approach is given by the mathematical school that recommends the use of computers and mathematical techniques to solve complex management issues and assist in the managerial decision-making process. Managers observe historical quantitative relationships and use quantitative techniques such as statistics, information models, and computer simulations to improve their decision making.
-
There are four major factors in leadership called Leader, Follower, Communication, and Situation. The success of the leader is dependent on how the leader is effectively able to communicate and motivate followers to perform desired tasks using the appropriate leadership style best suited for the given situation. Interdependencies and dynamics of these four factors of leadership must be considered by a leader to be effective.
-
Max Weber gave the theory of Bureaucratic Management in 1915. Bureaucracy is a specific form of organization defined by complexity, division of labor, professional management, and hierarchical management control. Weber's theory has two essential elements - organizational hierarchy and rules-based management. Weber made a distinction between authority and power and advocated that authority must be given to the most competent and qualified people.
-
McClelland's Theory of Needs is a human motivation theory which states that an individual's specific needs are acquired over time through our culture and life experiences. As per the three needs theory, these acquired needs significantly influence the behavior of an individual. The three main driving motivators are the needs for achievement, affiliation, and power.
-
Many different types of teams have been identified by social scientists. Managers may encounter the diverse types of challenges while managing different kinds of teams. Challenges associated with Cross-Functional Teams might be different from that of a Geographically Dispersed Team or a Virtual Team. This article explores some common categories and subtypes of teams.
-
Investment Theory of Creativity
Sternberg in the year 2006, proposed the investment and confluence theory focused on understanding creativity. According to the investment theory, creativity requires a confluence of six distinct but interrelated resources known as intellectual abilities, knowledge, styles of thinking, personality, motivation, and environment. It emphasizes that creativity is not about one thing, but about a system of things.
-
The best career choices are ones that match your values. Each person has several values that are important to him. These values are highly personal and knowing them provides a clearer sense of what's most important to you in your life and career. Career values are the beliefs you consider important from a work standpoint. Values help you understand what you want from a job? Explore a few examples of work values that can influence career path and job satisfaction.
-
Frederick Winslow Taylor started the “Scientific Management Movement”, and attempted to study the work process scientifically. Scientific management, also called Taylorism, was a theory of management that analyzed and synthesized workflows. It is a system for increasing the efficiency of manpower to its maximum potential and streamlining production to improve efficiency. This article explores this theory in more detail.
Explore Our Free Training Articles or
Sign Up to Start With Our eLearning Courses

About Us
Learning
© 2023 TechnoFunc, All Rights Reserved










